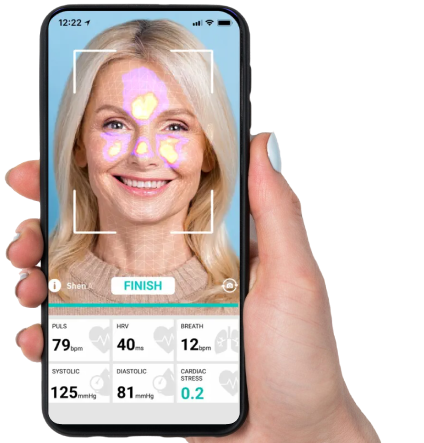
Yes, blood pressure and heart rate are related. Blood pressure is a measure of the force of blood against the walls of your arteries as the heart pumps it around the body. Heart rate is a measure of the number of times the heart beats per minute.
When the heart beats faster, it pumps more blood, leading to an increase in blood pressure. Conversely, when the heart beats more slowly, it pumps less blood, leading to a decrease in blood pressure. There are several mechanisms through which blood pressure and heart rate are related.
Baroreceptor reflex
One such mechanism works is through the baroreceptor reflex. It is a feedback loop that helps to maintain blood pressure within a narrow range. When blood pressure increases, pressure receptors in the arteries called baroreceptors send a signal to the brain to slow down the heart rate. When blood pressure decreases, the baroreceptors send a signal to the brain to speed up the heart rate. This helps to maintain blood pressure within a healthy range.
RAAS
Another mechanism through which blood pressure and heart rate are related is through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This is a hormonal system that helps to regulate blood pressure by constricting or dilating blood vessels. When blood pressure is low, the RAAS system is activated to constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure. When blood pressure is high, the RAAS system is activated to dilate blood vessels and decrease blood pressure.
Blood Pressure And Heart Rate Research
Several studies have examined the relationship between these two in humans. One such study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Its authors found that in a group of young, healthy adults, the first positive correlated with the second parameter.
Another relevant study was published in the Journal of Hypertension. The researchers found that in a group of older adults, the pulse was significantly correlated with both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Blood Pressure And Heart Rate: Not a fixed relationship
It is important to note that the relationship between heart rate and blood pressure is not fixed. It can vary depending on a number of factors, including physical activity, stress, and medications. For example, during exercise, the heart rate typically increases and the blood pressure may also increase.However, both should return to normal levels once the exercise is completed.
If the heart is damaged or not functioning properly, it may not be able to maintain normal blood pressure. This may affect your blood pressure. If you are concerned about your blood pressure or heart health, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional.
In general, when our BP goes up, heart rate may drop as a result of the baroreceptor reflex, described above. The heart rate may increase while the BP decreases through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
Reasons to call for medical assistance
It is generally not necessary to call 911 or your local emergency number solely because of an elevated heart rate. A heart rate that is consistently above 100 beats per minute is considered fast and may indicate an underlying medical condition. The normal range for heart rate can vary. It depends on a number of factors, including age, physical activity level, and overall health. A heart rate that is considered normal for one person may be too high or too low for another person.
It is always important to seek medical attention if, in addition to fast heart rate, you are experiencing any symptoms that are severe or that concern you. However, there are certain situations in which it is particularly important to seek immediate medical attention, such as:
- Chest pain or tightness: Chest pain or tightness can be a sign of a heart attack or other serious cardiac condition.
- Difficulty breathing: Difficulty breathing can be a sign of a serious respiratory condition, such as asthma or pneumonia.
- Sudden numbness or weakness: Sudden numbness or weakness, particularly on one side of the body, can be a sign of a stroke.
- Severe bleeding: Severe bleeding, such as from a cut or wound, can be a serious medical emergency.