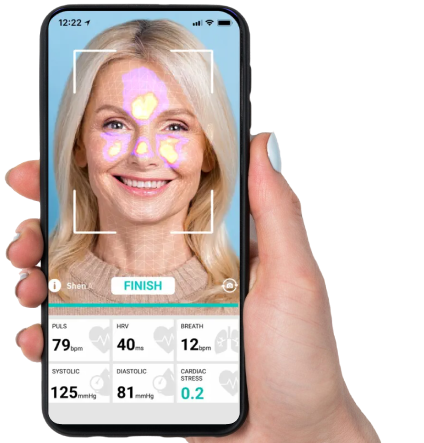
In my pursuit to review the latest heart health innovations, I stumbled upon this app called Heartscan. It makes snapshots of the chest vibrations that originate from the mechanical activity of the heart. The app targets people with heart arrhythmia. Heartscan employs seismocardiography, the technology invented in the 1980s. In that time, electrocardiography has won over the seismocardiography due to easy of use and cost of hardware. However, nowadays seismocardiography can be done with an iPhone, it is implemented in this seismocardiography app.
The interview with the seismocardiography app’s creator
How exactly does the seismocardiography app works? What new opportunities this opens to doctors and to patients? Why was the seismocardiography app developed? Read the full interview with Michal Barodkin, the man behind the Heartscan. He is a very interesting person to talk to. With three university degrees (in computer science, in economics, and an MBA) and several health tech projects in his portfolio, Michal stands out among typical startup founders. Also, he has a personal interest in heart health.
Speaking to Bloodpressure.me, Michal Barodkin said about the use of iPhone:
The recent development of micromechanical sensor systems has created this unique opportunity. The accuracy of the sensors in the average smartphone today reaches the level of scientific measuring equipment.
Recent lab-based data from clinical trials of other technologies has significantly lower accuracy, sampling frequency and a much higher noise level than we record with a regular smartphone today. The classic technology employed, electrocardiography, the ECG, has become widespread not because of its accuracy, but because of its simplicity.
For a long time there was no accessible hardware for recording heart vibrations with high enough accuracy. And it was already possible to use the electrical activity of the heart.
Independent scientific studies confirm that a seismic cardiogram is much more accurate in determining, for example, coronary heart disease than standard ECG and ultrasound and is comparable in accuracy to ECG and ultrasound of the heart under stress, when patients perform physical work during the measurement process.
Read the full interview here.
Seismocardiography. Background
Seismocardiography (SCG) is a non-invasive technique that measures the mechanical vibrations produced by the heart as it beats. These vibrations are recorded at the chest surface and provide valuable information about cardiac mechanics, including heart sounds, cardiac output, and the function of the heart valves. The technique has evolved significantly since its inception, with advancements in sensor technology and signal processing contributing to its development as a potential tool for routine cardiac monitoring.
Seismocardiography: towards the app
The concept of seismocardiography dates back to the early 20th century, with initial efforts focused on measuring heart-induced motion, including displacement, velocity, and acceleration. The term “seismocardiogram” was first used in the 1960s, and the earliest known use of the noun is from 1962. However, it was not until the 1990s that SCG began to gain attention as a potential clinical tool. The early methodology for obtaining SCG recordings and the initial findings were described in various studies, laying the groundwork for future research.
Recent Developments
Recent advancements in SCG have been driven by the need for new diagnostic tools to provide early detection and intervention for cardiovascular diseases, which are a major cause of death worldwide. The renewed interest in SCG has been fueled by the availability of low-cost, lightweight sensors, and the application of advanced signal processing and machine learning methods. These developments have enabled the creation of wearable SCG devices that can be used for long-term monitoring.
Physiological basis and signal characterization
SCG signals are believed to originate from various cardiac mechanical processes, including muscle contraction, valve movement, blood flow turbulence, and momentum changes. The characterization of SCG signals involves defining fiducial points that correlate with different cardiac physiological events, such as valve openings and closings. For instance, a study defined eight fiducial points in the SCG and correlated them with physiological events observed in ultrasound images, demonstrating the potential of SCG to characterize the cardiac cycle.
Clinical utility and challenges
SCG has shown promise in detecting and monitoring various cardiovascular conditions, such as coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, ischemia, and hemorrhage. The technique can provide complementary diagnostic information to other modalities like electrocardiography (ECG) and echocardiography. However, the complexity of SCG signals has introduced challenges in interpreting the data, and there is a need for the development and clarification of definitions, standards, and annotations.
Seismocardiography app. Future prospects
The future of SCG looks promising, with the potential to become a routine tool for cardiac assessment. Its advantages include low cost, ease of use, and the ability to provide a complete picture of cardiac function. The technology could enable early detection of cardiovascular diseases and facilitate home-based monitoring of cardiovascular health. Ongoing research is focused on improving the accuracy and reliability of SCG measurements, as well as developing algorithms for automated analysis of the signals.
Further reading
Here is the list of citations turned into a hyperlinked list with titles:
- Seismocardiography a new technique for recording cardiac vibrations concept method and initial observations
- A Comprehensive Review on Seismocardiogram: Current Advancements on Acquisition, Annotation, and Applications
- ECG-Free Heartbeat Detection in Seismocardiography Signals via Template Matching
- Nature Article on Seismocardiography
- PubMed Article on Seismocardiography
- NCBI Article on Seismocardiography
- MDPI Article on Seismocardiography
- Nature Article on Seismocardiography Research
- OED Definition of Seismocardiogram
- NCBI Article on Seismocardiography Technique
- Heartforce on Seismocardiography
- PubMed Article on Seismocardiography Development
- PubMed Article on Seismocardiography Applications
- European Heart Journal Digital Health on Seismocardiography
- IEEE Xplore Document on Seismocardiography
- IEEE Xplore Document on Seismocardiography Research
- Wiktionary Definition of Seismocardiography
- ResearchGate Article on Seismocardiography
- ScienceDirect Article on Seismocardiography