In 2023, Apple applied for a patent to measure blood pressure via earbuds. In the patent application for a biosensing device, the inventors refer to biological signals (biosignals). The inventors describe biosignals as electrical activity of the brain of a user. They will be collected on the go, and promise new, truly exciting possibilities in healthcare, though they raise a number of ethical concerns.
Heart health to be measured via earbuds
Out of many stated measurements, two are directly relevant to heart health.
- Blood volume pulse (BVP). This is measured using photoplethysmography (PPG). IT provides information about heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV).
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) typically measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Blood pressure
How Will Earbuds Measure Blood Pressure?
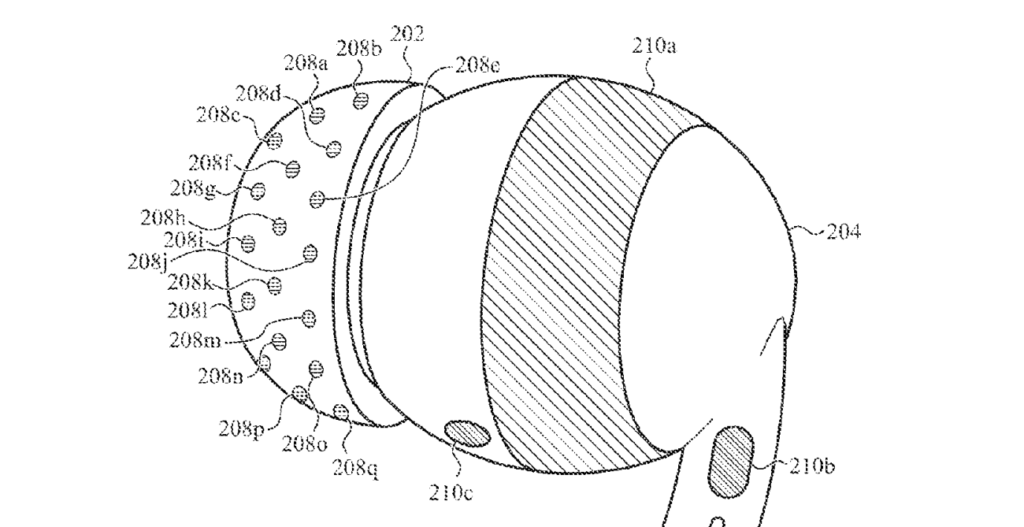
The Apple’s patent outlines electrodes on a non-planar surface within the earbuds. This system includes a sensor circuit and a switching circuit. The latter can connect different subsets of electrodes to measure electrical activity. SharpBrains state that this configuration is crucial for accurate blood pressure measurements by detecting physiological changes through the ear’s vascular system.
The sensors in the new earbuds are designed to maintain firm contact with the ear through 3D, spring-loaded mechanisms. SciTechDaily writes that the sensors are covered with a hydrogel film that helps collect sweat, for biochemical measurements. These electrophysiological sensors will record the brain’s electrical activity, Gadgets 360 concludes. These sensors can adapt to the ear’s movements and maintain necessary contact to avoid data loss. SciTechDaily believes it will ensure continuous monitoring of blood pressure. The hydrogel film will be employed to act as a cushion. This film ensures the sensors have a stable and effective interface with the skin, enhancing the accuracy of the measurements.
The earbuds will feature a multimodal wearable bioelectronic platform. It will record both physical and biochemical information simultaneously. This platform includes sensors that can measure brain activity, physical exertion, and possibly blood pressure by analyzing the ear’s physiological and biochemical signals.
Apple & Blood Pressure: The Technology Behind
Optical Sensors
The earbuds will likely use photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors. PPG sensors work by emitting light into the skin and measuring the amount of light that is either absorbed or reflected back. This data can be used to determine blood flow and, consequently, blood pressure.
Acoustic Sensors
The earbuds may also incorporate acoustic sensors that can detect biosignals such as heart sounds. These sensors can pick up the subtle sounds of blood flow and heartbeats, which can be analyzed to infer blood pressure levels.
The PPG and acoustic signals will be processed by advanced algorithms to provide accurate assessments of blood pressure readings. The algorithms will analyze the time it takes for a pulse wave to travel between different points in the ear, which is known as pulse transit time (PTT). PTT is inversely related to blood pressure, allowing the device to estimate blood pressure levels.
Pressure Sensors
The patent mentions the use of pressure sensors that can measure the force exerted by blood flow within the ear canal. This method can provide a direct measurement of blood pressure by detecting changes in pressure as blood pulses through the arteries.
Apple & Blood Pressure: In-Ear Microphones
The earbuds will use in-ear microphones to capture heart sounds, similar to how a stethoscope works. These sounds will be transmitted to a smartphone or another device via Bluetooth, where they will be analyzed to determine blood pressure.
Conclusion
The Apple earbuds, as they are described in the patent application, are designed to provide continuous blood pressure monitoring, which is a significant advantage over traditional cuff-based methods that only provide intermittent readings. This continuous monitoring can help users track their blood pressure throughout the day and detect any significant changes in real-time.