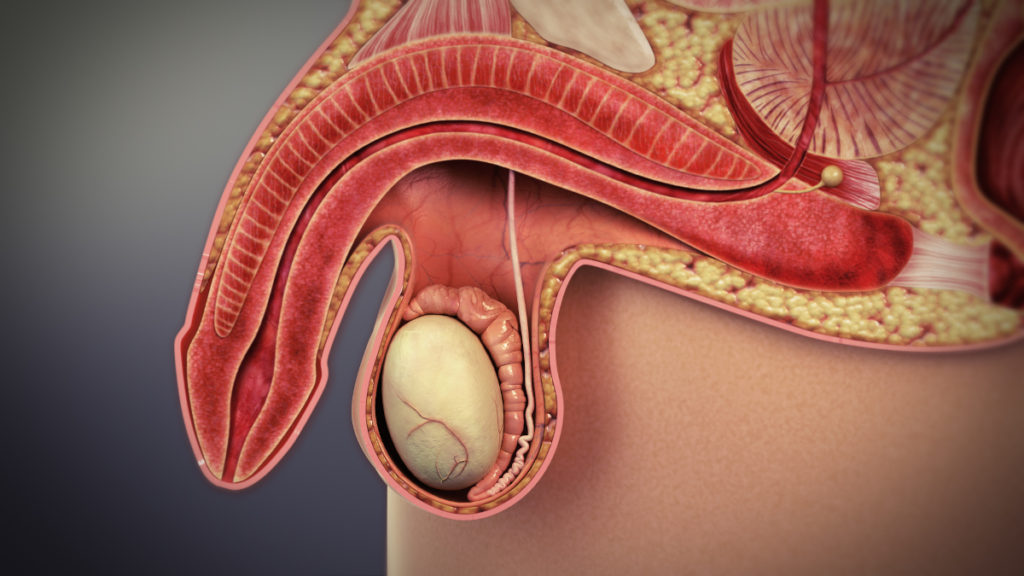
Check with your doctor before taking medications for erectile dysfunction (ED). A number of drugs are available to treat erectile dysfunction, including sildenafil (Viagra), vardenafil (Levitra, Staxyn) and tadalafil (Cialis). Generally, pill forms are considered safe for men with high blood pressure who are otherwise healthy.
For men with severe cardiovascular disease or high blood pressure who have difficulty urinating or have other lower urinary tract problems, erectile dysfunction drugs aren’t recommended. It is not recommended to take erectile dysfunction drugs with nitrates, which are used to treat chest pain. Blood pressure can drop dangerously if you do so.
The increased use of medication among older men, and the side effects of many drugs related to ED, contribute to ED. Medication is estimated to cause 25% of all ED.
Blood pressure drugs are near the top of the list of drugs that can cause erectile difficulties. In some cases, ED can be caused by BP drugs such as thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, and beta-blockers. These drugs decrease blood flow to the penis and make getting an erection difficult. However, Alpha-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and angiotensin-receptor blockers rarely cause ED.
It has even been suggested that blood pressure drugs have more of a psychological effect than a physical one. It’s possible that anxiety about a man’s health, rather than the medication, may trigger ED after he starts taking a new medication. Men may be more likely to recognize abnormal side effects if they are aware of possible side effects.
According to Harvard Special Health Report Erectile Dysfunction, a study in the European Heart Journal examined men newly diagnosed with heart disease, but without ED, who started taking the beta-blocker atenolol (Tenormin). Almost one-third of the study participants reported having an ED after being told about the blood pressure drug’s sexual side effects. Comparatively, only 3% of those who were not told the drug’s name or side effects experienced ED.